A low pass filter is placed on the signal wires between a signal and an electronic device such as a DAQ module. It stops frequencies greater than the cut off frequency from entering the DAQ module analog or digital inputs.
How does a low pass filter work?
The key term in a low pass filter circuit is the CUT OFF FREQUENCY. The cut off frequency is the frequency above which no variation of voltage with respect to time may enter the circuit. For example, if a low pass filter had a cut off frequency of 30 Hz, the type of interference associated with line voltage (60Hz) would be filtered out but a signal of 25 Hz would be allowed to pass.
Also, in a digital circuit, a low pass filter might be used to de-bounce an input from a momentary contact button pushed by a person, or even a relay closure connected to a counter-timer input.
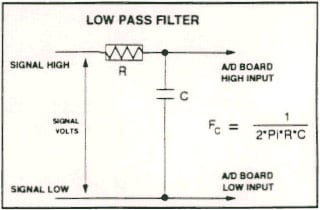
A low pass filter may be constructed from on resistor R and one capacitor C. The cut off frequency Fc is determined according to the formula:
Fc= 1/2*Pi*C
R= 1/2*Pi*C*Fc
See the following diagram
 LOW PASS FILTER
LOW PASS FILTER


